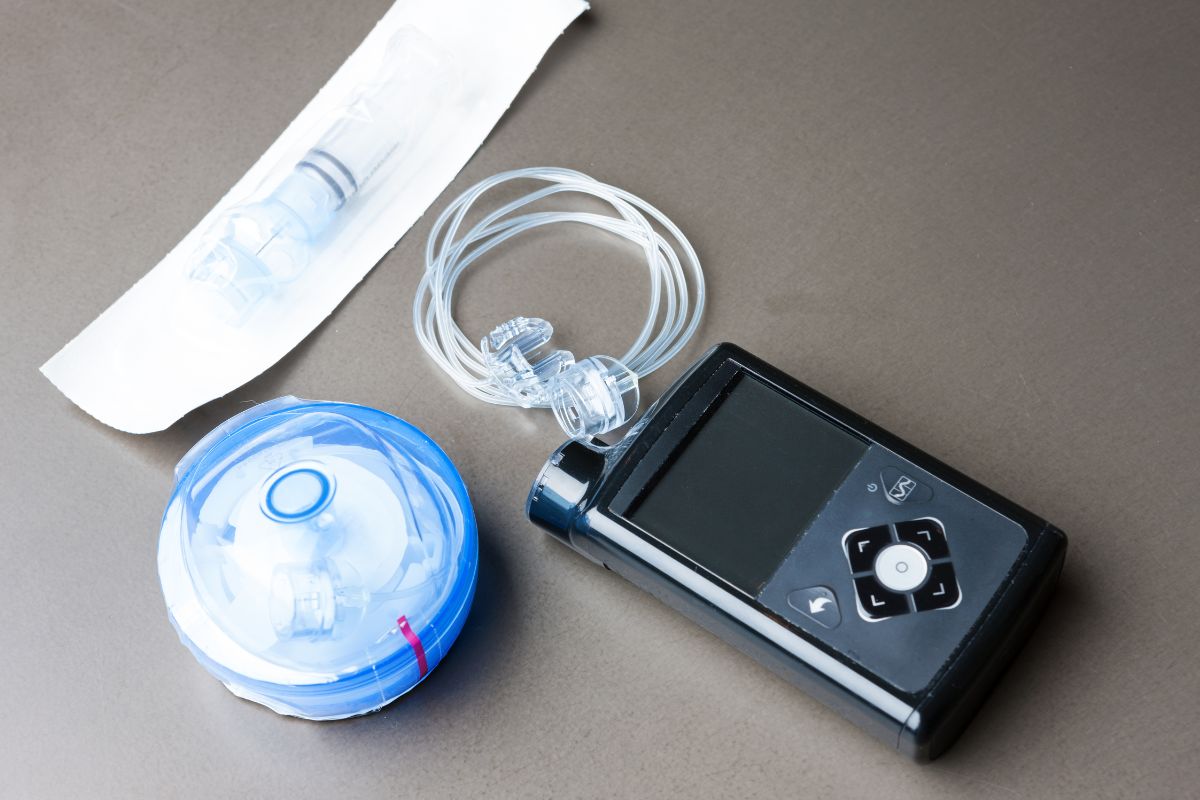
Insulin pumps are small electronic devices that deliver insulin through a tiny tube that goes under the skin.
They were first introduced in the 1980s. How do they actually work?
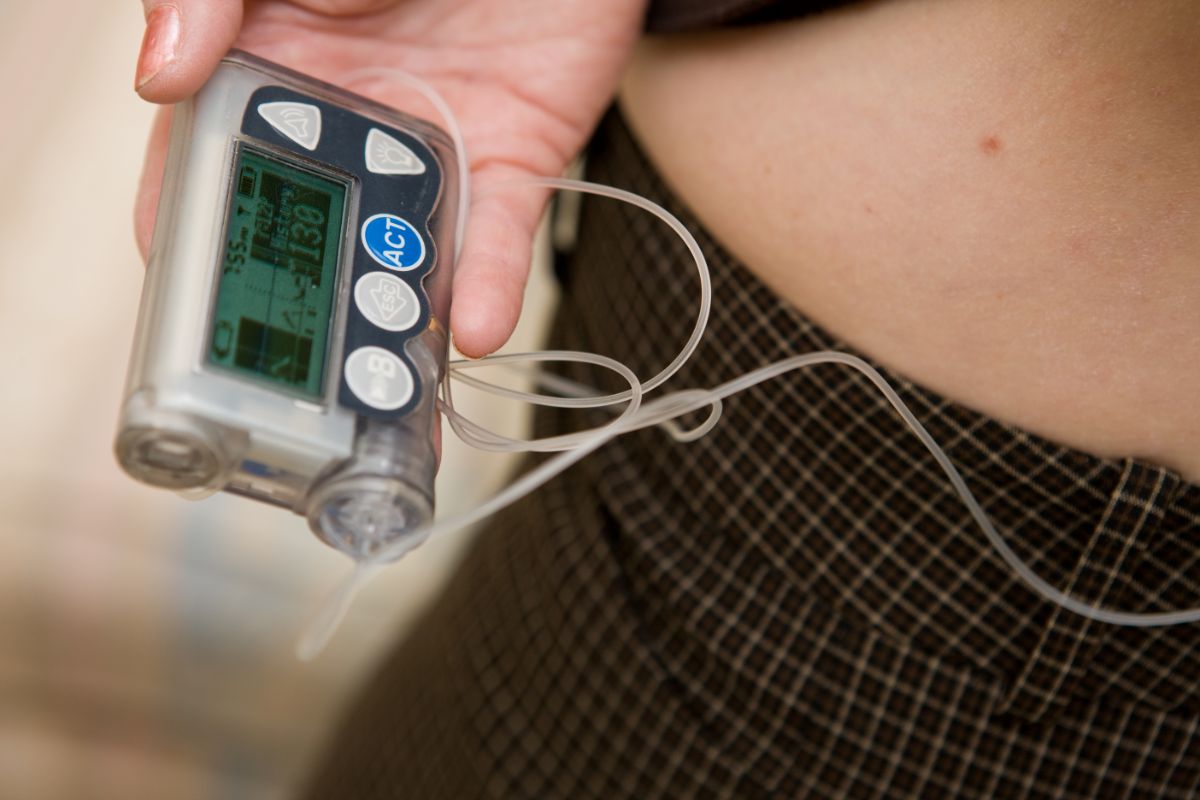
The device delivers insulin in the same way your pancreas does: a steady flow throughout your day and night, called Basal Insulin, and an extra dose when you need it, called Bolus Insulin.
You program the pump to deliver either a continuous flow of insulin or a series of smaller doses.
If you eat more carbohydrates than usual, you can program a bigger bolus to cover them all.
A bolus can lower high blood sugar at any time, even if you haven’t eaten anything recently.The pump consists of two parts: the transmitter and the receiver.
The transmitter connects to the receiver via Bluetooth technology.
The transmitter contains all the electronics necessary to communicate with the receiver and the battery.
A user programmable memory chip stores information regarding the type of insulin, dosage, and other settings. The receiver is attached to the skin using a special adhesive patch.
Advantages
A pump is an insulin delivery device that has many advantages.
Firstly, they are usually connected to a computer and can be controlled via smartphone apps.
There are two types of pumps: external and implantable.
External pumps are attached to the body using a belt or harness. Implanted pumps are implanted inside the body and are worn on the abdomen making them convenient and accessible.
Using a pump means fewer injections which is a real bonus for those who dislike needles.
In addition, they help manage low blood sugar episodes, commonly known as hypoglycemia and can reduce the risk of long term complications.
They can also help prevent the dawn phenomenon or early morning increase in blood sugar.
Another advantage is that they are easy to program and adjust. They are not affected by weather changes making them super flexible.
They are also comfortable and discreet.
Pumps can be used by diabetics with type 1 diabetes and can also be used during pregnancy. Furthermore, they are more affordable than injections.
It’s worth remembering that if you use a pump you should still have extra insulin avaiable in injectable form in case the pump gets broken or fails to work.
People that choose pumps enjoy the flexibility and freedom it provides compared with injections.
For example, if you are going to engage in a strenuous activity or do an excercise class you have the option of changing the basal dose.
This means you can control blood glucose levesl much easier. It also allows more flexibility aorund eating, requiring just a small adjustment to accomodate this.
Pumps are the best choice for babies and toddlers because they are easy to use and have a low risk of injury.
Because caregiveers are with babies all the time it’s easy to monitor. There are also features that allow you to lock out the child to prevent them from pushing buttons accidentally.
Disadvantages
Pumps require regular maintenance and training. Training involves going through the setup procedure, learning how to use the device, and practicing at home.
Maintenance includes replacing batteries and cleaning tubing. There are also additional costs associated with the pump itself.
It’s wise to rememebr that a continuous glucose monitor (CGM) may not be right for everyone. It requires an external sensor attached to your skin.
Some people dislike the sensation of the sensor under their skin and are uncomfortable with the idea of wearing a device all day long and others feel uncomfortable with the number of steps required to calculate insulin doses.
Some people don’t like checking their blood sugars 4x/day and aren’t sure they want to do the work necessary to figure out insulin dosed, carbs, and physical activities.
The pump requires frequent monitoring because it does not provide any long-lasting insulin supply.
If a child has an issue with the insertion site, it may require medical attention. Parents should check the pump frequently to monitor blood sugar levels.
A child may need extra assistance when inserting a new pump site or troubleshooting a problem.
For many people, the pump is too visible and gets in the way of daily activities. Some find the needle is painful and sometimes it hurts more than an ordinary syringe needle.
Children often find it hard to push the button, and the needle is larger than a normal syringe.
Pumps are not always the perfect solution and anyone who chooses to use a pump must be willing to make decisions when problems occur.
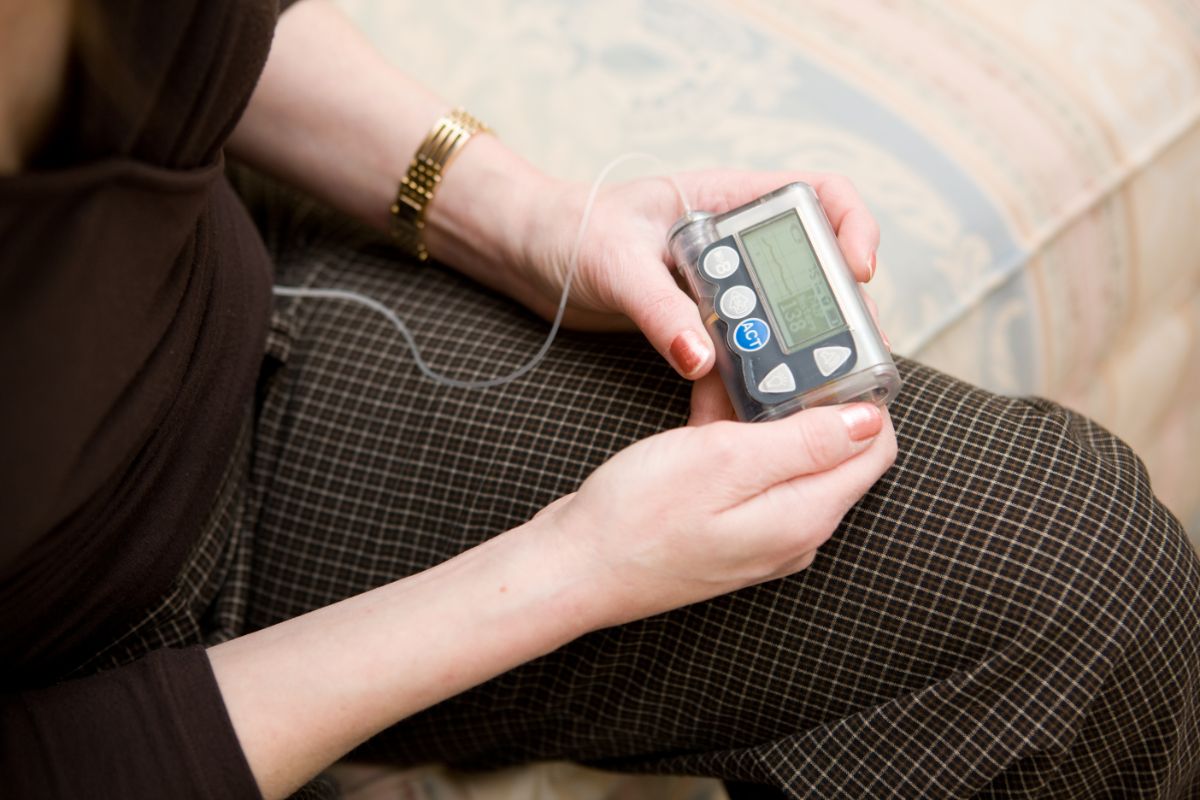

Best Pumps
If you do decide that using a pump is the best option for you, how can you decide which pump ot go for?
Insulin pumps come in many different shapes and sizes. You need to choose one that fits your lifestyle.
As youself some question such as: Is ease of use important to you? How long will you keep using the pump? Will you be traveling often?
If so, consider a tubeless design.
A traditional pump requires an infusion set, which needs to be changed every time you inject.
Tubeless designs require a prefilled cartridge, which is inserted into the device. Both types have pros and cons.
Traditional pumps require less frequent changes, but they’re harder to clean. Tubeless pumps are easier to clean, but changing them is more complicated.
Some pumps are reusable and others disposable. Reusable pumps are cheaper, but require cleaning before each use.
Disposable pumps are more expensive, but there is no risk of cross-contamination. Both types of pumps can be connected to a CGM device, which helps users manage their diabetes.
Some pumps also allow interaction with a smartphone or laptop.
Affordability
Insurance policies vary widely. Some cover insulin pumps while others do not. Check your policy carefully before buying a pump.
If you have trouble covering the cost, ask your doctor or pharmacist about assistance.
Insulin pumps are expensive, and many manufacturers provide financial assistance to people who cannot afford them.
Find out what your options are. You might also qualify for government programs that help low-income patients pay for medications.
In Summary
In the age of modern medicine it’s great to have a choice of treatments for illnesses. Insulin pumps are a great invention and may be just the answer for those that hate needles.
- Understanding Male Reproductive Health: A Complete Guide - February 2, 2025
- Simple Healthy Skin Habits for Radiant Skin - December 6, 2024
- Unlocking the Connection Between Nutrition and Mental Health - December 3, 2024