Various tests can be used to diagnose heart disease, and today we will explore some of these options and all you need to know regarding the testing process.
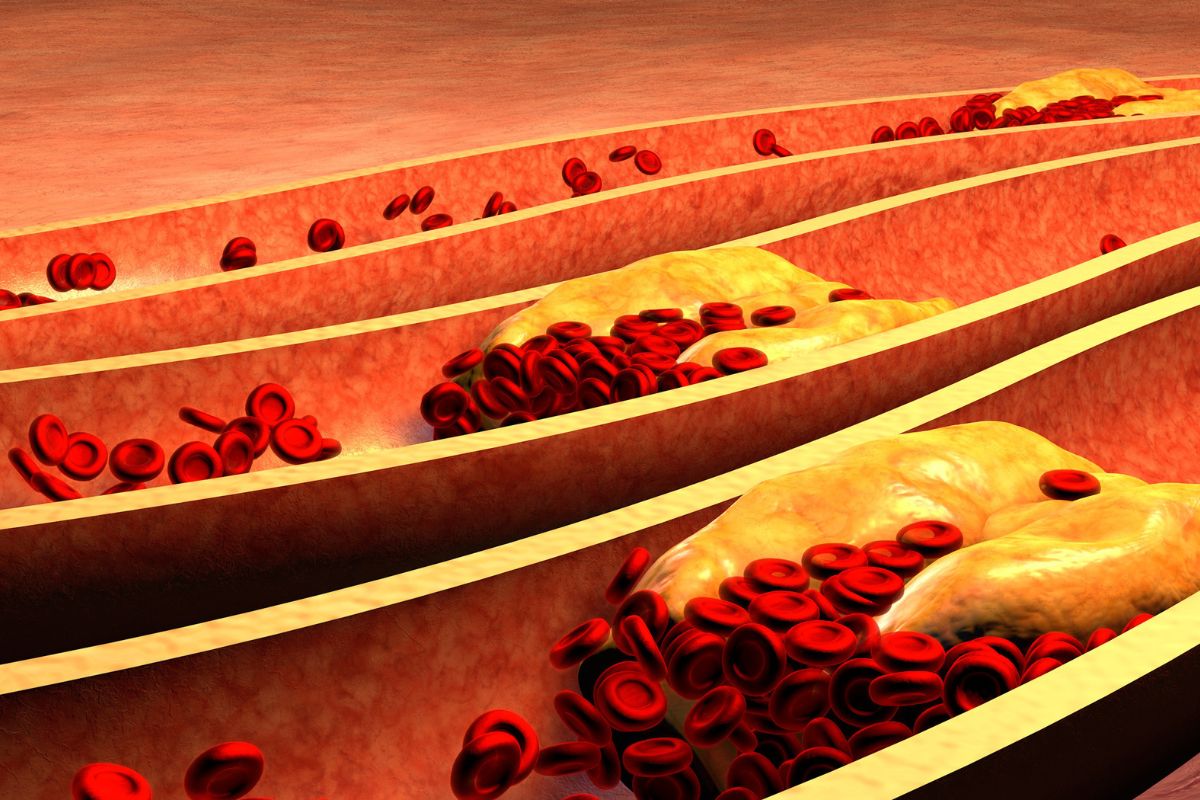
One of the leading causes of death in the world is coronary heart disease which can be caused in several ways. This is the process in which your heart blood supply is blocked or interrupted via fatty substances that are situated in the arteries.
This blockage results in fatty deposits building up over time, which then is known as atherosclerosis.
Some of the most common causes of heart disease are typically down to lifestyle factors. you are at higher risk of heart disease if you are a smoker, regularly drink excessive amounts of alcohol (see also ‘Beer Belly – Does Alcohol Really Cause Weight Gain?‘), and conditions like high cholesterol, high blood pressure, or diabetes.
This can then be correlated to those that are overweight or obese, and so maintaining a healthy lifestyle is the first step in preventing heart disease.
What Are The Symptoms Of Heart Disease?
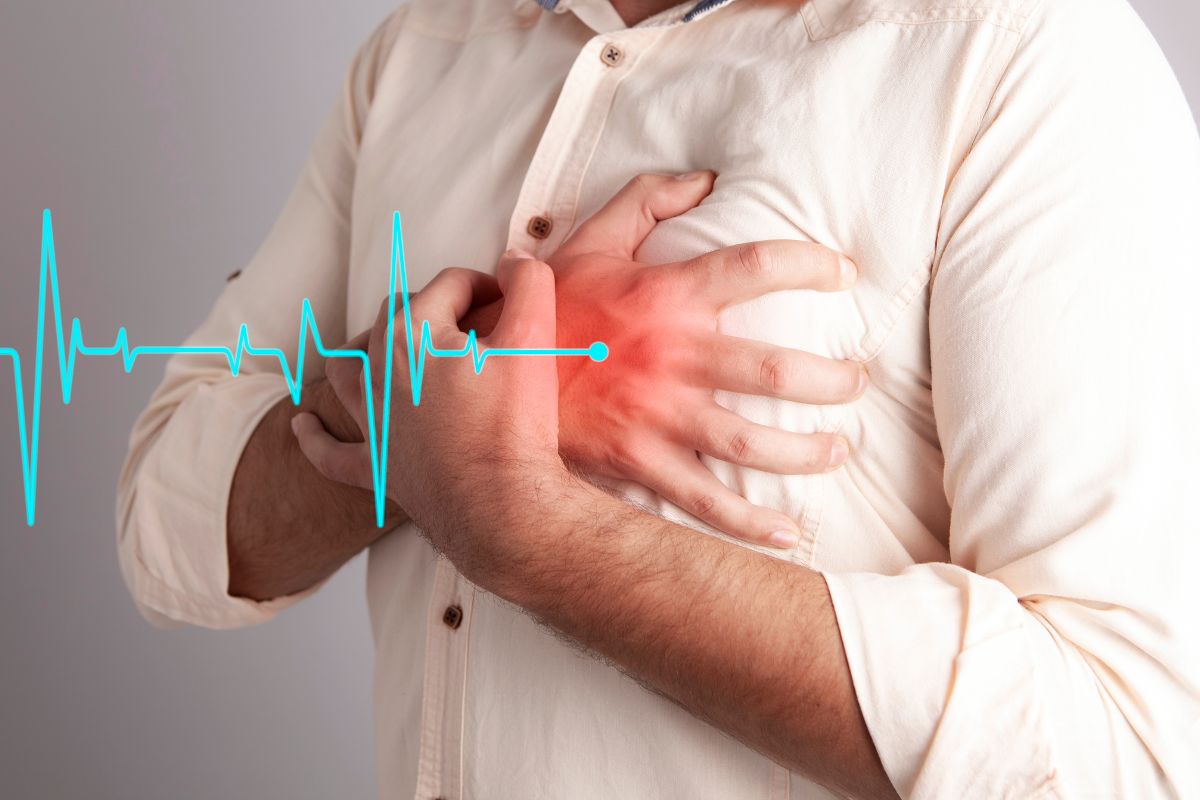
Like a lot of conditions, it can be problematic to diagnose heart disease as it can vary from person to person, with the symptoms either developing gradually over weeks or months or even having a sudden onset.
One of the most common symptoms of heart disease Is pain in the chest, also known as angina. you may also feel a shortness of breath, general pain throughout the body, feeling nauseous, or light-headed and faint.
Another tricky problem with diagnosing heart disease is that some people may not have any symptoms before realizing they have heart disease, which is why it is important to maintain a healthy lifestyle to avoid complications down the line.
Diagnosing Heart Disease
The First port of call is to seek out the advice of your doctor, who will likely perform several exams on you as well as take a detailed history of your medical past and family history.
There are a common set of tests that are carried out for the diagnosis of heart disease, and besides the most common ones such as blood tests and a chest x-ray, you may receive one of the following tests if your doctor suspects heart disease:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG) is a painless test that will record the electrical signals of the heart. This is a useful tool to use as it can spot abnormal heart rhythms. You will typically have an ECG while you’re resting, but the doctor nights commit to an exercising electrocardiogram which is known as a stress electrocardiogram.
- Echocardiograms are another exam that is non-invasive and will use sound waves to show images of the heart structure. This is a useful test as it will show the doctor how your heart beats and pumps blood around the body.
- Holter Monitoring is silver 20 CG but it’s portable that you can wear in your day-to-day life which will continuously monitor your heart rhythm. This is usually carried out for around 24 to 48, which can sometimes be extended to up to 3 days. limitations of a regular ECG are that it may not detect issues with your heart rhythm and so the portable option could spot something that the ECG missed.
- A doctor might Also carry out a stress test. Similar to the stress test with the ECG, this test will raise your heart rate by exercise or a controlled medicine. At the same time, a hot test will be carried out to check how your heart responds to the physical or stress incurred by the medicine.
- CT scans are another common test carried out for diagnosing heart disease. This is where you will lie inside of a machine that will send an x-ray tube inside the machine that rotates around your body collecting images.
- MRIs can be used to create detailed images of the heart. They are done by using magnetic fields and computer-generated radio waves. These machines are notoriously loud and sometimes you will wear headphones to mask the loud noises that occur during the test.
- Cardiac catheterization tests involve a short tube that is inserted into a vein in your leg or arm. You then have a hollow tube that is longer which is inserted into the short tube. The catheter will then be carefully threaded through the artery until it reaches the heart which will then use x-ray images to examine it.
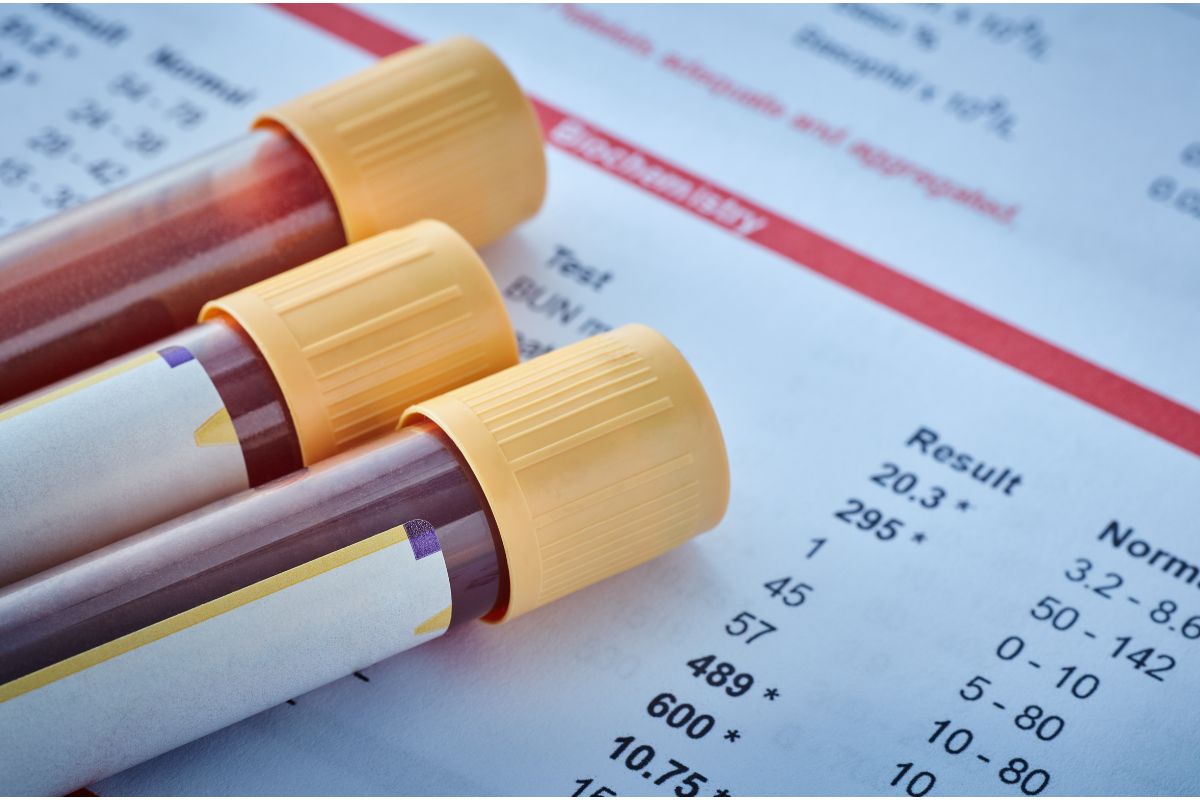
Blood Tests
As already mentioned, a likely route of testing will be a blood test, and it will help determine your risk of heart disease and can also evaluate other systems in your body that can also be linked to heart disease.
A blood test will test for several blood markers. One of the most common blood markers tested will be your total cholesterol, which includes low-density lipoprotein often referred to as the bad cholesterol and high-density lipoprotein (HDL) which is commonly referred to as the good cholesterol.
Along with these markers, you also like to get your triglycerides checked. High levels of triglycerides can lead to too many complications in the body.
Which can increase the risk of heart disease, but also stroke, and metabolic syndrome.
Another Common market-tested in a blood test is the c reactive protein (CRP), which is a marker for inflammation in the body.
This is where your liver produces this protein as a response to infection or injury, and a link between heart disease and c-reactive protein is that when fatty deposits clog your arteries, this increases your risk factor for heart disease.
You might also be tested for homocysteine, which is another protein used to build and maintain tissue. The problem is when you have too much homocysteine which is shown to increase your risk of getting heart disease and having a stroke.
Final Thoughts
Learning About the warning signs of heart disease is the first step in identifying a potentially life-threatening condition, however, you should never self-diagnose yourself without first speaking with your doctor.
Seek help from the professionals who will likely carry out several tests that we have listed above.
- Understanding Male Reproductive Health: A Complete Guide - February 2, 2025
- Simple Healthy Skin Habits for Radiant Skin - December 6, 2024
- Unlocking the Connection Between Nutrition and Mental Health - December 3, 2024


![When Is A HIV Test Conclusive? Everything That You Need To Know When Is A HIV Test Conclusive? [Everything That You Need To Know]](https://alphanutrition.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/When-Is-A-HIV-Test-Conclusive-Everything-That-You-Need-To-Know-150x150.jpg)