Arthritis is estimated to affect over 90 million adults worldwide, which have been diagnosed by doctors as arthritis or containing arthritis-like symptoms.
And so finding some dietary options to help alleviate symptoms can be a minefield, as there’s nothing worse than spending money on useless supplements.
Today will explore some of the best arthritis supplements we recommend, and your best options moving forward.
Sometimes when we are faced with a difficult situation in terms of a chronic health condition, simply throwing money at supplements can feel like you are working towards something. Still, you may just be wasting money on things that are not helping you.
We have done our best to look at the data and determine what has been shown to help with arthritis via research. Here are the best options.
One thing to mention, before we get into the list of supplements is that you should not fall for any other traditional treatments that your doctor has recommended.
These are supplements that are designed to be supplemented alongside your current treatment plan, and shouldn’t be construed as the only solution to your condition.
And finally; speak to your doctor before making any changes to your lifestyle, especially any changes to your diet or supplementation program.
Glucosamine
The most commonly used supplements for arthritis are glucosamine and chondroitin.
Glucosamine is a supplement that is derived from shellfish and studies have shown that glucosamine sulfate can reduce the rate of joint tissue (collagen) degrading.
That’s what the symptoms of osteoarthritis are.
Glucosamine is that evidence is limited, however, a recommended high dose of 3000 mg of glucosamine sulfate could be an option to reduce joint degradation.
However, the research suggests this is prevalent in athletic populations that can be in high-impact sports such as running.
One of the most common side effects of glucosamine supplementation is flatulence.
One thing to note about glucosamine is that it cannot cure arthritis, but can certainly slow the progression of the condition.
Chondroitin
We already touched on chondroitin as it is typically paired with glucosamine as a combination therapy to help ease joint pain and stiffness as well as other symptoms that are commonly found in osteoarthritis.
Similar to glucosamine, the studies that have been used are poorly designed or subject to potential errors due to the low number of participants.
therefore this option cannot reset a certain whether it may help or not although we had seen anecdotally some help for some populations.
When comparing glucosamine and chondroitin, studies have continued to be by contrast as to which is most effective, and when compared head-to-head the results showed they can offer equivalent pain relief.
Therefore it is down to the individual as to whether they feel they should try a trial-and-error system where they try one option first followed by the other and see which has the better effect.
A typical dose of chondroitin is around 1000 to 1200 MG a day.
Omega-3 Oil
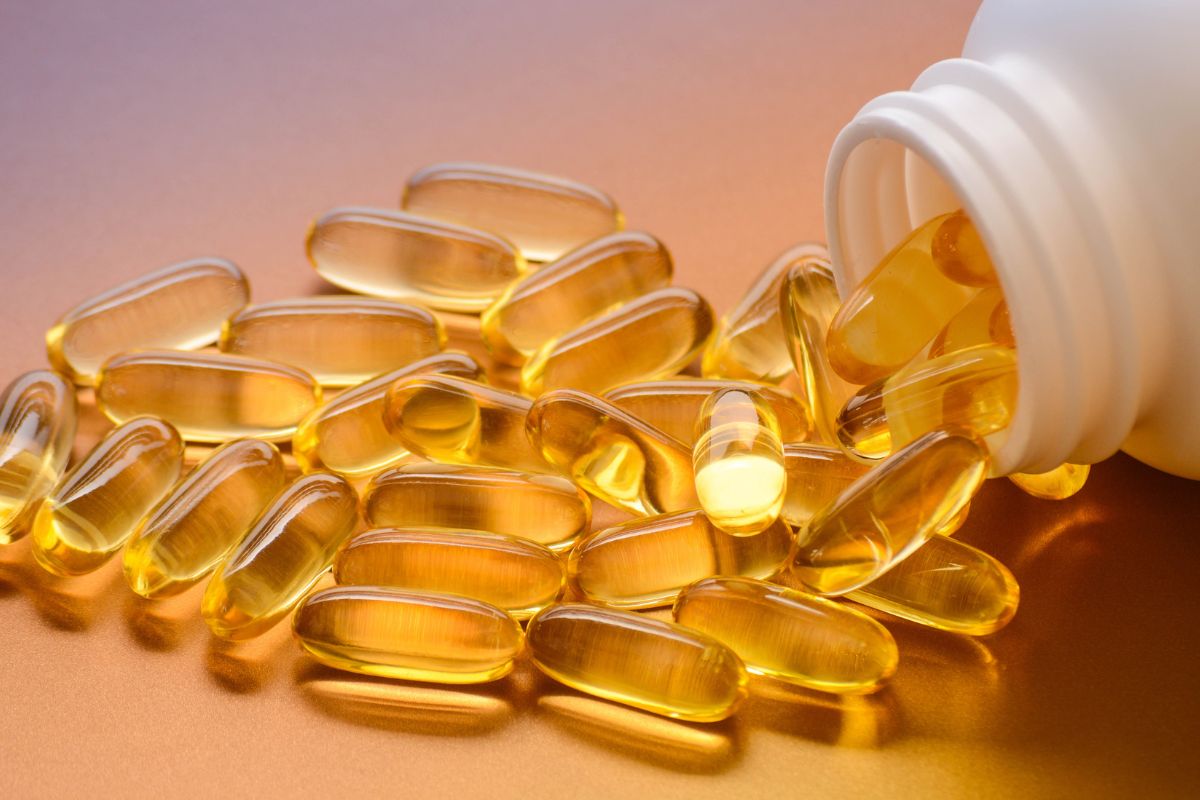

One of the most well-researched supplements in the world is Omega-3 fatty acids. typically found in fish as polyunsaturated fats which have been shown to have a potent anti-inflammatory effect on the body.
Research has shown that these anti-inflammatory effects are most potent for those with rheumatoid arthritis as this form of arthritis is mostly driven by inflammation in the body.
Many have taken Omega-3 fatty acids and have reported a reduction in joint pain swelling as well as stiffness in rheumatoid arthritis, and for those that take a lot of pain relievers such as ibuprofen, Taking fish oils is a powerful alternative to this route.
The good thing about omega-3 oil is that there are more health benefits than just an anti-inflammatory effect.
Fish oil especially can cause a reduction in triglyceride levels and has even been shown to reduce blood pressure in those with hypertension.
A benefit of omega-3 oil is they can improve mood in those with major depressive symptoms, although research into my depression is limited and has been shown to be unclear if it affects these.
along with its anti-inflammatory benefits for rheumatoid arthritis, can also be shown to reduce the symptoms in lupus.
This makes omega 3 oil A worthwhile supplement for general health, let alone rheumatoid arthritis.
There are many ways to get omega-3 oil into your diet, the most common way is to supplement with fish oil.
However, If you are a vegetarian or vegan you can opt for an algae-based supplement, however, it is worth noting that algae are not as effective as it requires the Alpha linoleic acid to turn into EPA and DHA which are the properties of omega 3.
You can also find omega-3 in flaxseed As well as chia seeds which are also in the short-chain form of alpha-linolenic acid.
When looking for an omega-3 supplement you want to ensure that the EPA and DHA are what you are searching for as this is where the majority of the health benefits lie. 2-3 grams of EPA and DHA per day are recommended.
SAM-e
S-adenosyl-methionine Is a compound that is naturally anti-inflammatory for the body and can help relieve pain. It has been shown to be as good as reducing pain that NSAIDs can deliver.
A typical dose of SAM-e is around 1200 mg per day and will take a few weeks to take effect.
Vitamins
Vitamins A, C, and E as well as vitamins D and K are good options for supporting overall health. Although evidence for anti-inflammatory properties is lacking, these vitamins will help support bone health, especially vitamin D and vitamin K.
Curcumin
We also recommend incorporating curcumin into your diet, which is a Spice popularly used in Asian dishes. You can also supplement with it, and It is best taken with black pepper for the best absorption with food.
Final Thoughts
Whilst not a complete panacea, these supplements can help support those that are suffering from different forms of arthritis. Remember to consult your doctor before making any changes to your diet or supplementing your routine
- Understanding Male Reproductive Health: A Complete Guide - February 2, 2025
- Simple Healthy Skin Habits for Radiant Skin - December 6, 2024
- Unlocking the Connection Between Nutrition and Mental Health - December 3, 2024