Arthritis is a common condition affecting millions of people worldwide, and the most common symptoms include classic signs such as joint pain, stiffness, swelling, and redness.
In many cases, X-rays are amongst the most common methods used to diagnose arthritis, and these can be useful in showing whether or not the bones around the joints are damaged.
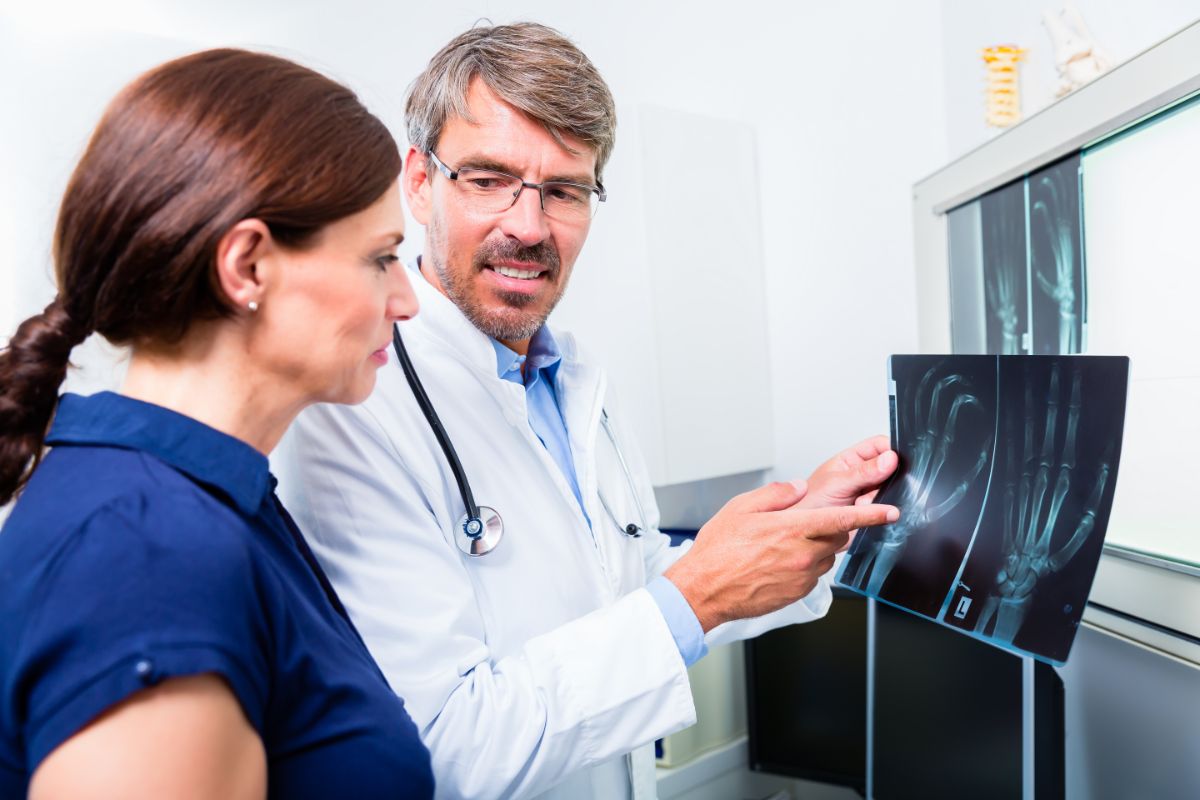
While it is true that x-rays can provide valuable information, they also expose patients to unnecessary radiation, and they can be less effective at detecting the early signs of arthritis.
So just how effective are they really, and are there any alternatives? We took a closer look.
What Is Arthritis?
Arthritis is defined by the American College of Rheumatology (ACR) as “a group of diseases characterized by inflammation of one or more joints”.
It is estimated that over 50 million Americans have some form of this condition, and that about of these, around a third, will go on to develop rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
The main symptom of RA is chronic pain, which usually starts with small areas of inflammation in the affected joints.
This leads to damage to the cartilage covering the ends of the bones, causing them to rub together, and eventually leading to bone erosion.
There are a number of different types of arthritis, including:
- Osteoarthritis (OA): This is the most common type of arthritis, and affects nearly half of all adults aged 65 years and older. It is caused by wear and tear on your body, and can affect any part of your skeleton. Symptoms include joint pain, stiffness, and loss of movement.
- Rheumatoid arthritis (RA): This is an autoimmune disease where the immune system attacks healthy tissue in the body. It causes painful, swollen joints, and may lead to long-term problems if left untreated.
- Gout: Also called ‘acute gouty arthritis’, this occurs when too much uric acid builds up in the bloodstream. As a result, crystals form within the joints, causing intense pain and swelling.
- Psoriatic arthritis: This is another auto-immune disorder that causes the skin and nails to become inflamed, and it often involves the joints.
- Juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA): This is a rare but serious condition that mainly affects children under the age of 16. It is characterized by inflammation of the joints and can cause severe disability and even death.
Other forms of arthritis may include fibromyalgia, lupus, and Lyme disease.
How Is Arthritis Diagnosed?
There are several ways to diagnose arthritis. Your doctor will start by asking you questions about your medical history, and looking at your joints.
They may ask you to describe the nature of your pain and to show them what happens when you move your joints.
You may also need to undergo a physical examination, during which they will examine your joints and other parts of your body.
The following tests may then be carried out:
- Blood Tests: These can help identify certain conditions associated with arthritis, such as infections or heart disease.
- X-rays: These images can reveal changes in your joints, and can indicate whether there is damage to the cartilage or bone.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): This test uses magnets and radio waves to produce detailed pictures of your muscles, tendons, ligaments, and nerves.
- Ultrasound Scan: A special machine sends high-frequency sound waves through your body, allowing doctors to see inside the structures of your joints.
- Computerized Tomography (CT) scan: This is used to view internal organs, bones, and soft tissues. It produces a series of cross-sectional images from different angles.
- Bone Scans: These use x-ray beams to create images of the bones in your wrist, knee, and ankle. The images can reveal areas of increased density, which could indicate osteoporosis or arthritis.
How Effective Is An X-Ray To Diagnose Arthritis?
One of the most common methods for diagnosing arthritis is to perform an x-ray. An X-Ray is a picture taken using radiation, which shows details of the bones, including their size and shape.
If you have been diagnosed with arthritis, your doctor may order an X-Ray to check how well your joint’s cartilage has healed after treatment.
X-Rays can be effective in diagnosing arthritis, but they may not be the best option in all cases.
For example, if you have only mild symptoms, or if you don’t want to expose yourself to any more radiation than necessary, this method may not be suitable – as with any procedure of this type, there is a risk of exposure to radiation in order to get the images required.
If you do decide to go ahead with an X-Ray, it is important to remember that it does not replace a clinical diagnosis.
In some cases, it may be difficult to distinguish between specific types of arthritis based solely on the results of an X-Ray.
What Treatment Options Are Available For Arthritis?
There are many treatments available for people who suffer from arthritis.
However, no single treatment works for everyone, and you may have to try a range of types of treatment to find the best solution for your body. Some treatments work better than others depending on the type of arthritis you have.
Non-Surgical Treatments For Arthritis
There are many non-surgical options available for treating arthritis.
These include:
- Resting And Stretching: Resting and stretching exercises can help reduce stiffness and improve movement. You should also make sure you’re getting enough sleep at night.
- Exercise: Regular exercise helps keep joints flexible and strong. Try swimming, walking, cycling, or other forms of aerobic activity.
- Medication: There are several medications that can be prescribed by your doctor to treat pain and inflammation. Examples include NSAIDs (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs), corticosteroids, and opioids.
Surgery
Surgery is sometimes recommended when other treatments haven’t worked, or when your condition is severe.
This includes arthroscopic surgery where small instruments are inserted into the affected area to remove damaged tissue. Other surgical procedures include total hip replacement and partial knee replacement.
Final Thoughts
Arthritis can be a painful condition, but early diagnosis and the correct treatment boost your chances of retaining mobility in the affected area and can improve your quality of life.
If you suspect that you may have arthritis, see your doctor as soon as possible, and they can help to decide the best course of treatment for your condition.
- Understanding Male Reproductive Health: A Complete Guide - February 2, 2025
- Simple Healthy Skin Habits for Radiant Skin - December 6, 2024
- Unlocking the Connection Between Nutrition and Mental Health - December 3, 2024